Recent searches
Loading...
1348-1236 - Sagittal section. 1. Brain. 2. Corpus callosum. 3. Septum lucidum. 4. Thalamus. 5. Mamillary body. 6.Mesencephalon. 7. Pons. 8. Medulla oblongata. 9. Spinal cord. 10. Cerbellum. 11. Frontal sinus. 12. Ethmoid cells. 13. Concha. 14. Sphenoida
1348-1075 - This electron micrograph depicts a number of Marburg virions responsible for causing Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever.
1348-1572 - Hyperflash in the two nuclei and particularly the putamen, and the two thalamus.
1348-1650 - Gastric pains. Stomach of a patient having swallowed pebbles.
1348-1327 - Patient having ingested a tineless fork. The stem of the fork, located in the stomach cavity, shows holes due to the corrosive action of the stomach's hydrochloric acid. The head of the fork has pierced the greater curvature
1348-1328 - Patient having ingested a tineless fork. The stem of the fork, located in the stomach cavity, shows holes due to the corrosive action of the stomach's hydrochloric acid. The head of the fork has pierced the greater curvature
1348-1423 - Miracidium larva of the liver fluke (fasciola hepatica) viewed in SEM.
1348-1425 - Miracidium larva of the liver fluke (fasciola hepatica) viewed in SEM.
1348-1234 - Sagittal section. 1. Brain. 2. Corpus callosum. 3. Septum lucidum. 4. Thalamus. 5. Mamillary body. 6.Mesencephalon. 7. Pons. 8. Medulla oblongata. 9. Spinal cord. 10. Cerbellum. 11. Frontal sinus. 12. Ethmoid cells. 13. Concha. 14. Sphenoida
1348-1424 - Miracidium larva of the liver fluke (fasciola hepatica) viewed in SEM.
1348-1326 - Patient having ingested a tineless fork. The stem of the fork, located in the stomach cavity, shows holes due to the corrosive action of the stomach's hydrochloric acid. The head of the fork has pierced the greater curvature
1348-1065 - Transmission electron micrograph of influenza A virus, late passage.
1348-1436 - Measles virus (of large size) and SV40 virus (of small size), TEM. This electron micrograph reveals both a paramyxovirus measles virus, and virions of the polyomavirus, simian virus SV40 (smaller circles)
1348-1152 - Syphilis bacterium. Treponema pallidum subsp pallidum on cultures of cotton tail rabbit epithelium cells Sf1Ep
1348-1648 - Gastric pains. Stomach of a patient having swallowed pebbles.
1348-1570 - Hyperflash in the two nuclei and particularly the putamen, and the two thalamus.
1348-1655 - Gadolinium enhanced MRI-T1. Coronal cut-away. Idiopathic metastases causing generalized epileptic seizures in a 40-year old man.
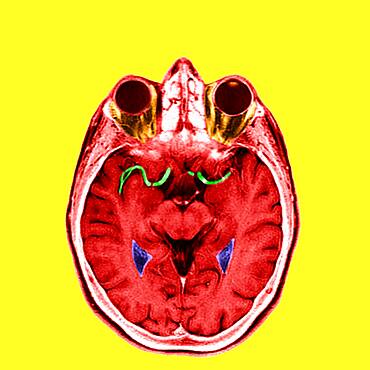
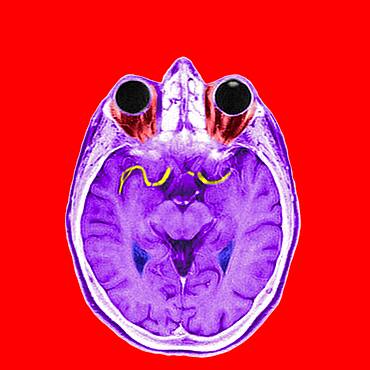
1348-1609 - Highlight of the anterior and medium cerebral arteries.
1348-1610 - Highlight of the anterior and medium cerebral arteries.
1348-117 - Cowpox virus, used for the preparaton of a smallpox vaccine (TEM). Electron micrograph of a Vaccinia Virus. Vaccinia virus is normally confined to cattle, but is conveyed to humans through vaccination
1348-573 - Senior woman measuring her blood pressure.
1348-571 - Senior woman measuring her blood pressure.
1348-394 - Doctor explaining to a patient the result of her mammogram.
1348-371 - Female patient consulting for cervical pain.